Acute cholecystitis is a medical condition that affects the gallbladder and can cause severe pain and discomfort. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of acute cholecystitis, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or simply want to learn more about this condition, read on to gain valuable insights.
What Is Cholecystitis?
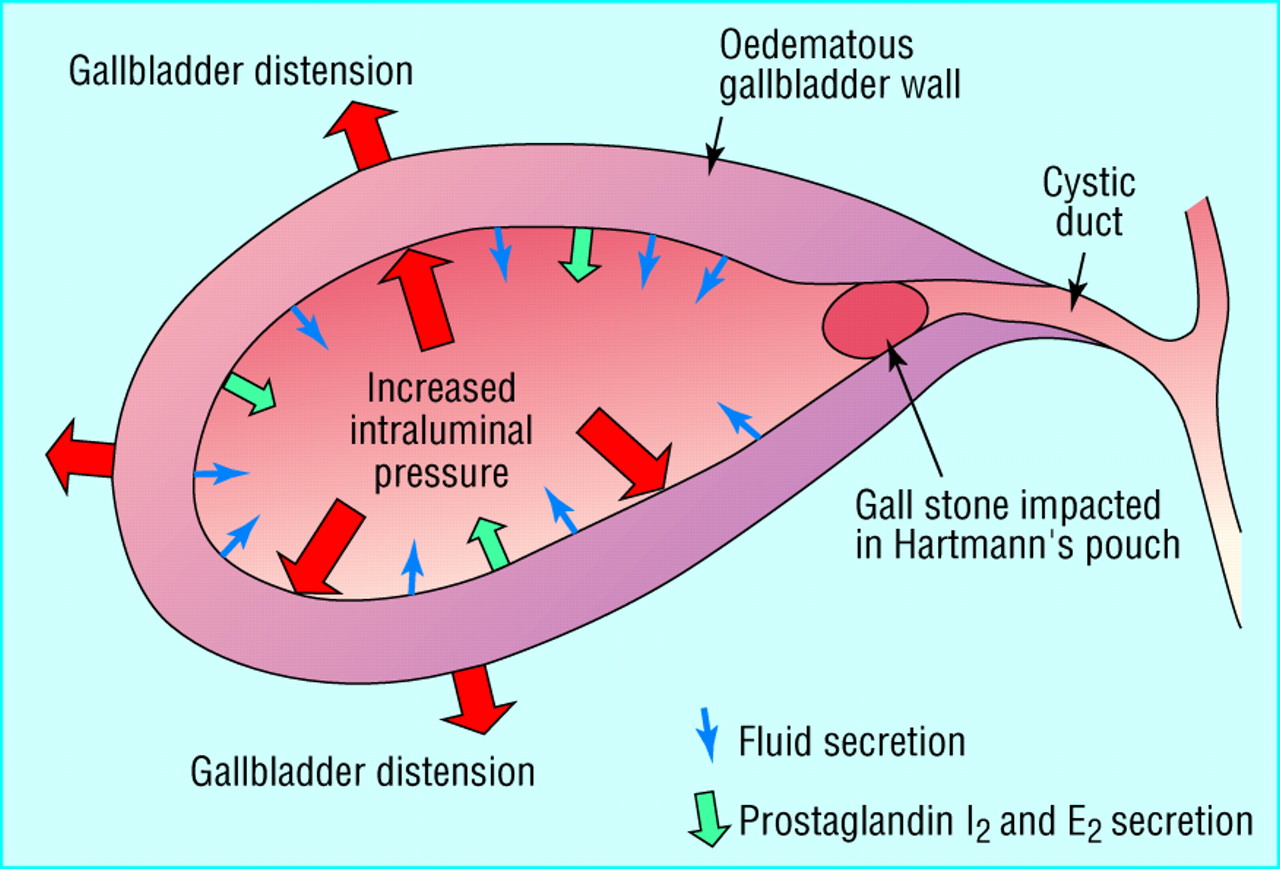
Acute cholecystitis is an inflammatory condition of the gallbladder, which is a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder plays a crucial role in storing bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats in the food we eat. When the bile ducts leading to the gallbladder become blocked or inflamed, it can lead to acute cholecystitis.
Cholecystitis Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of acute cholecystitis is essential for early diagnosis and prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Severe Abdominal Pain: The most prominent symptom of acute cholecystitis is intense pain in the upper right or center of the abdomen. This pain may radiate to the back or right shoulder.
- Fever: Many individuals with acute cholecystitis develop a fever, which is a sign of infection or inflammation.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Patients often experience nausea and may vomit due to the discomfort and pain.
- Abdominal Tenderness: The abdomen may be tender to the touch, especially in the area around the gallbladder.
- Jaundice (in severe cases): In rare instances, a blockage of the bile duct can cause jaundice, which results in yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Causes of Acute Cholecystitis
Understanding the causes of acute cholecystitis can help you take preventive measures. The primary causes include:
- Gallstones: The most common cause of acute cholecystitis is gallstones. These small, hard deposits can block the bile ducts or irritate the gallbladder lining, leading to inflammation.
- Bile Duct Blockage: Other factors such as tumors or injury can also block the bile ducts, causing cholecystitis.
- Infection: In rare cases, an infection in the gallbladder can lead to acute cholecystitis.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes and obesity increase the risk of gallstones and, consequently, acute cholecystitis.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cholecystitis
If you suspect you have acute cholecystitis or are experiencing symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical exams, blood tests (CBC) , and imaging tests such as ultrasound.
Treatment options for acute cholecystitis may include:
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for observation and treatment.
- Pain Management: Pain medications such as NSAIDs (Paracetamol) are often prescribed to manage the intense abdominal pain.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present, antibiotics will be administered.
- Surgery: In most cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy, is the most effective long-term treatment. This can often be done laparoscopically, leading to a quicker recovery.
Acute cholecystitis can be a painful and concerning condition, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most individuals can recover fully. It’s important to be aware of the symptoms and risk factors and to seek medical attention if you suspect you have acute cholecystitis. By doing so, you can ensure a quicker and smoother recovery process.
FAQs
1. What is acute cholecystitis?
- Acute cholecystitis is an inflammatory condition of the gallbladder, typically caused by gallstones or blockage of the bile ducts.
2. What are the common symptoms of acute cholecystitis?
- Common symptoms include severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal tenderness, and, in severe cases, jaundice.
3. What causes acute cholecystitis?
- The primary causes are gallstones, bile duct blockage (due to various factors), infection, and underlying medical conditions like diabetes and obesity.
4. How is acute cholecystitis diagnosed?
- Diagnosis often involves physical exams, blood tests, and imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans.
5. Can acute cholecystitis be treated without surgery?
- In some cases, early treatment with antibiotics and pain management may provide temporary relief, but surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is the most common and effective long-term treatment.
6. What is laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder through small incisions. It usually allows for a quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
7. Is acute cholecystitis a life-threatening condition?
- While acute cholecystitis can be serious and lead to complications if left untreated, it is not typically life-threatening with prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment.
8. Can acute cholecystitis recur after gallbladder removal?
- No, once the gallbladder is removed, the source of gallstones and inflammation is eliminated, reducing the risk of acute cholecystitis recurrence.
9. Are there any dietary changes or lifestyle modifications to prevent acute cholecystitis?
- Maintaining a healthy weight and a balanced diet low in saturated fats can help reduce the risk of developing gallstones, a common cause of acute cholecystitis.
10. How long is the recovery period after gallbladder removal surgery? – Recovery time can vary, but many people can resume normal activities within a week or two after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. However, individual recovery times may vary.
Remember that these FAQs provide general information, and individual cases may vary. If you suspect you have acute cholecystitis or have questions about your specific situation, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.