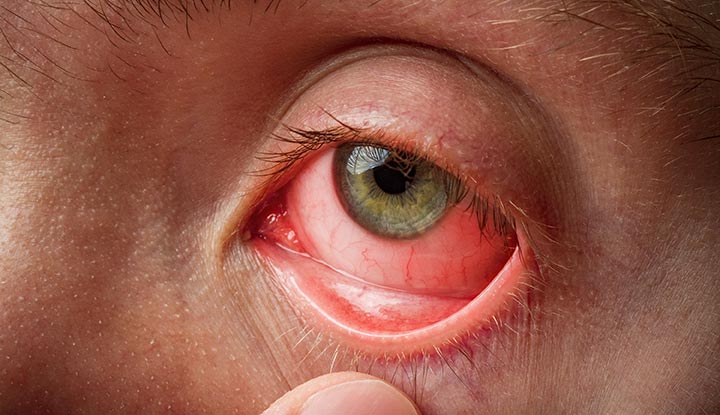
Pink eye is an infection of the transparent membrane (known
as the conjunctiva) of your eye, when blood vessels become inflamed, that causes itchy, red
and painful eyes. This is usually caused by bacteria, viral infections. Allergic reactions or
exposure to irritants can also cause pink eye. Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis are highly
contagious and can easily spread from person to person.
In some cases, pink eye recovers on its own. However, in few cases a doctor has to be
consulted. It is highly recommended that he or she does not rub their infected eye as it can
increase the redness.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis
Redness in the eye
Increased tears from the affected eye
Burning in the eye
Itchiness in the eye
Thick yellowish discharge from the eyes
Diagnostic Tests For conjunctivitis
Pink eye is usually diagnosed based on patient history and a
comprehensive examination of the eye. Allergy test for due to allergy.
Prevention
Avoid touching your eyes with your hands. Wash your hands thoroughly and
frequently. If you do not have access to a sink, use hand sanitizer. Change pillowcases often,
do not share eye makeup or personal eye care products, and do not reuse tissues or hand
towels on your face. Follow your eye doctor’s instructions about proper contact lens care.
treatment of conjunctivitis
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: This will clear out within two weeks. Your doctor may give you
medications, in the form of an ointment or eye drops, to speed up the process of
recovery. - Viral conjunctivitis: There is no specific treatment for viral conjunctivitis. Your doctor
may prescribe medications to ease the itching and burning. When conjunctivitis is viral, it
usually starts with one eye and then infects the other eye within three to four days. As it
usually clears up in two weeks. - Allergic conjunctivitis: eye drops that control allergic reaction or help prevent
inflammation.
FAQs:
1. What is pink eye (conjunctivitis)?
Pink eye, or conjunctivitis, is an inflammation of the thin, clear layer of tissue called the conjunctiva that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inner surface of the eyelid.
2. What causes pink eye?
Pink eye can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergies, or irritants like smoke and chemicals. Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis are highly contagious and can spread through personal contact, touching infected surfaces, or respiratory droplets.
3. What are the common symptoms of pink eye?
Common symptoms of pink eye include redness in the white part of the eye, itching or irritation, increased tearing, a gritty feeling, discharge (clear, yellow, or green), and crusting of the eyelids or lashes, especially upon waking.
4. Is pink eye contagious?
Yes, pink eye can be highly contagious, especially viral and bacterial forms. It can spread through direct or indirect contact with the eye secretions of an infected person, such as touching the eyes or sharing towels, pillowcases, or makeup.
5. How is pink eye diagnosed?
A healthcare provider typically diagnoses pink eye through a thorough examination of the eyes, reviewing symptoms, and discussing any recent exposure to irritants or infected individuals. They may also take a sample of eye discharge for further testing.
6. How is pink eye treated?
Treatment for pink eye depends on the cause. Viral conjunctivitis usually resolves on its own and is managed symptomatically. Bacterial conjunctivitis often requires antibiotic eye drops or ointment. Allergic conjunctivitis may be treated with antihistamines or other allergy medications.
7. How can I prevent pink eye?
To prevent pink eye, practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently, avoiding touching your eyes, and not sharing personal items like towels or eye makeup. If you have pink eye, follow proper hygiene to prevent spreading the infection.
8. Can pink eye cause long-term vision problems?
In most cases, pink eye does not cause long-term vision problems. However, severe or untreated cases can lead to complications such as corneal ulcers or conjunctival scarring, which may affect vision if not managed promptly.
9. When should I seek medical attention for pink eye?
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you experience severe symptoms, worsening redness or pain, sensitivity to light, blurred vision, or if you suspect a bacterial infection. If you’ve been in contact with someone diagnosed with contagious conjunctivitis, seeking medical advice is prudent.
10. Can pink eye affect both eyes at the same time?
Yes, pink eye can affect both eyes simultaneously, especially if the cause is a contagious virus or bacteria. It’s common for the infection to spread from one eye to the other. Proper hygiene and prompt treatment can help minimize the spread and severity of the infection.