Tinnitus, commonly known as ringing in the ears, is a prevalent and often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characteristic feature is that the origin of this sound is within the patient.It is not a disease itself but rather a symptom of an underlying issue.
I. Tinnitus Signs and Symptoms:
Tinnitus manifests in various ways, and individuals may experience different sensations in their ears. The primary symptom is the perception of sound when there is no external source. Common manifestations include:
- Ringing: Persistent or intermittent ringing in one or both ears.(Usually unilateral but can also affect both ears)
- Buzzing: A low-frequency humming or buzzing sound.
- Whistling: High-pitched tones resembling the sound of a whistle.
- Clicking: Repetitive clicking noises, akin to the sound of a clock.
Sound may vary in pitch and loudness and may be described by the patient as roaring, hissing, swishing, rustling or clicking type of noise.Tinnitus can be subjective, where only the affected individual hears the noise, or objective, where a healthcare professional can also hear the sound during examination.Tinnitus is more annoying in quiet surroundings, particularly at night, when the masking effect of ambient noises from the environment is lost
Types Of Tinnitus
Subjective: which can only be heard by the patient
Objective: which can also be heard by the examiner with the use of a stethoscope
II. Causes of Tinnitus:
Understanding the root causes of tinnitus is crucial for effective management. Tinnitus can be a symptom of an array of conditions, including:
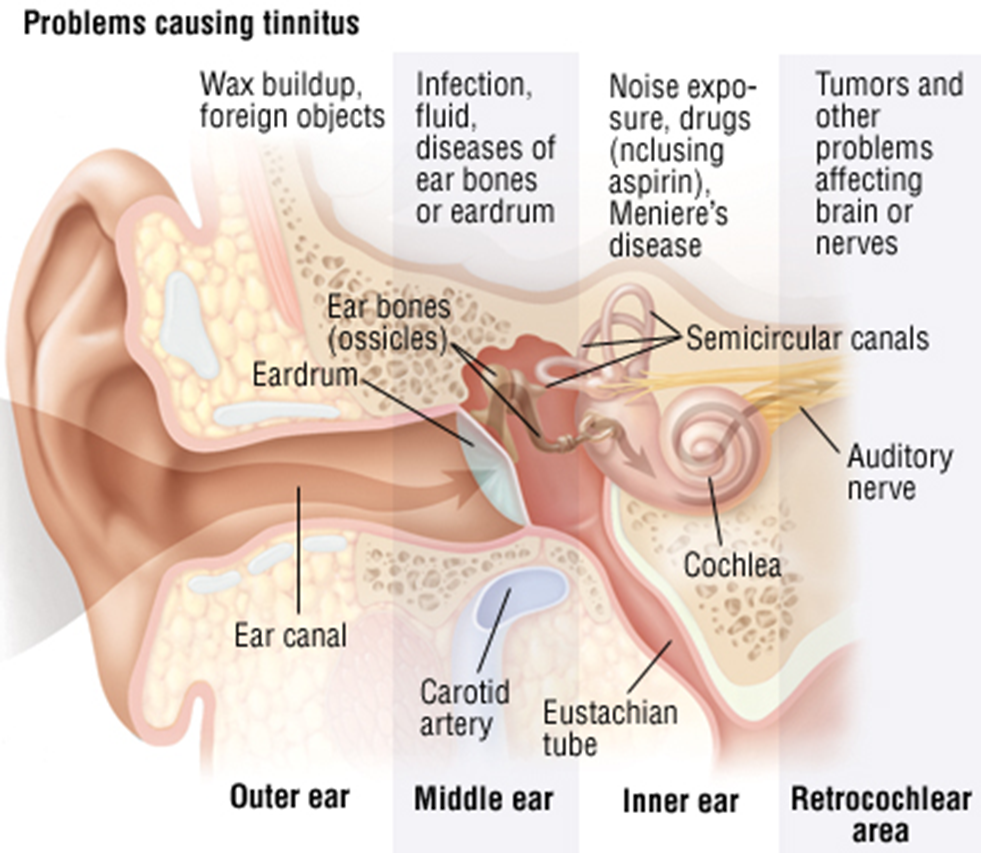
Subjective tinnitus may have its origin in the external, middle or internal ear, VIIIth cranial nerve or the central nervous system.Systemic disorders like anaemia, arteriosclerosis, hypertension and certain drugs may act through the inner ear or central auditory pathways.In the presence of conductive hearing loss, the patient may hear abnormal noises in the head during eating, speaking or even respiration
Objective tinnitus is less frequently seen. Vascular lesions e.g. glomus tumour or carotid artery aneurysm cause swishing tinnitus synchronous with pulse
Tinnitus synchronous with respiration may occur due to abnormally patent Eustachian tube (Patulous Eustachian Tube PET).
Sometimes, tinnitus is psychogenic and no cause can be found in the ear or central nervous system.It can be temporarily abolished by pressure on the common carotid artery
Some other Causes Include:
- Age-related hearing loss: Gradual deterioration of hearing with age.
- Exposure to loud noises: Prolonged exposure to loud environments or sudden loud noises.
- Earwax blockage: Buildup of earwax leading to hearing difficulties.
- Hearing loss due to injury or infection: Damage to the auditory system from injury or infection.
- Medications: Certain medications, especially those with ototoxic effects, can contribute to tinnitus.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like Meniere’s disease or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can lead to tinnitus.
III. Diagnosis:
If you suspect you have tinnitus, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. Diagnosis typically involves a thorough examination of your medical history, a physical examination, and, in some cases, imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to rule out underlying structural issues.
IV. Tinnitus Treatment
Since tinnitus is a symptom, not a disease, we aim to diagnose and treat the underlying cause, several strategies can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Addressing underlying causes: Treating the root cause of tinnitus, such as hearing loss or earwax buildup.
- Hearing aids: For individuals with hearing loss, hearing aids can amplify external sounds, making the internal tinnitus less noticeable.
- Sound therapy: Using white noise or other soothing sounds to mask or distract from the tinnitus noise.
- Counseling: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of tinnitus.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms, although results vary.
Tinnitus Maskers
Can be used in patients with no hearing loss.Use of these maskers for a short time may provide a symptom free interval for several Tinnitus Maskers are worn like hearing aids.
V. Tinnitus Prevention:
Preventing tinnitus involves adopting healthy hearing habits:
- Protect your ears: Use ear protection in noisy environments and limit exposure to loud sounds.
- Monitor medications: Be aware of the potential ototoxic effects of certain medications.
- Manage stress: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate tinnitus, so adopting stress-reduction techniques is beneficial.
